- Category
- Latest news
US Fines Haas Automation $2.5 Million for CNC Shipments to Sanctioned Russian Entities
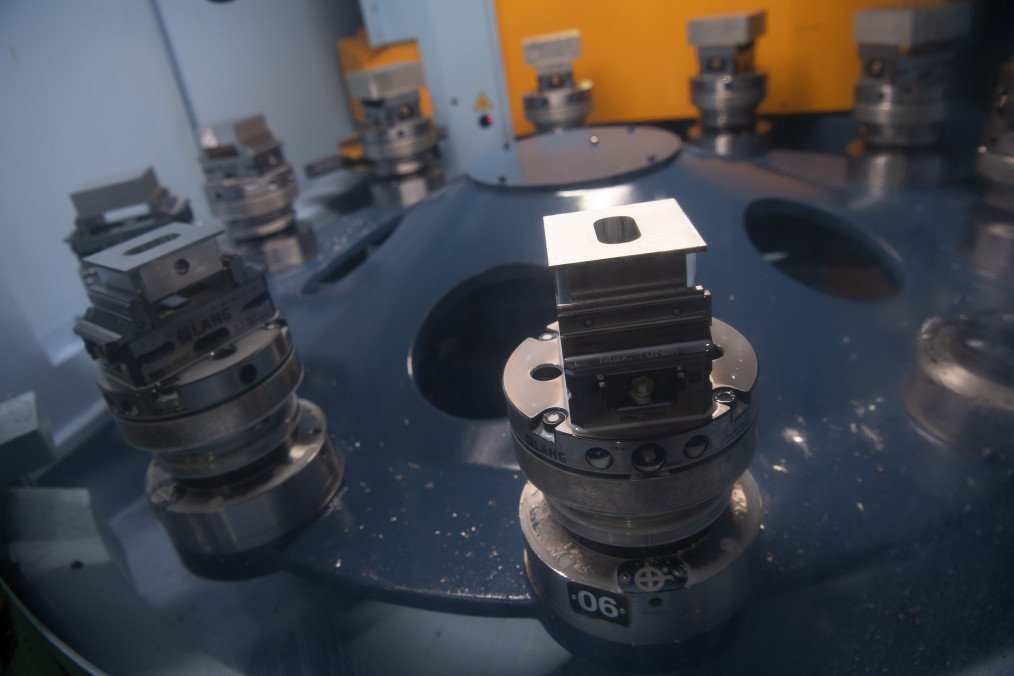

Haas Automation, a US manufacturer of CNC (computer numerical control) machine tools, has been fined by the United States for violating sanctions during Russia’s war in Ukraine.
On January 17, the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) and the Bureau of Industry and Security announced a combined fine of more than $2.5 million for unauthorized shipments of CNC parts to sanctioned entities in China and Russia.
Investigators found that between December 2019 and March 2022, Haas Automation supplied 41 CNC components to service machines operated by entities on US sanctions lists.
The OFAC stated that these shipments undermined international sanctions enforcement efforts and contributed to the military capabilities of Russia.
Allegations against Haas Automation were first made public in March 2023 by Denys Hutyk, Executive Director of the Economic Security Council of Ukraine (ESCU), and Agiya Zagrebelska, ESCU’s Policy Director, during a PBS NewsHour report.
ESCU analysts presented evidence that Haas products were being supplied to Russian enterprises through the distributor “Abamet” even after Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine. The findings were later shared with US authorities.
Haas Automation denied the allegations following the PBS NewsHour report, stating that all sales to Russia complied with export controls and sanctions. The company maintained that it had ceased direct business with Russia after the February 2022 invasion.
However, in January 2025, Haas Automation acknowledged 41 violations of the Export Administration Regulations. The company cooperated with the investigation and implemented corrective measures, which resulted in a reduced penalty.
“The Haas Automation case is an important signal for global corporations,” said Hutyk, adding, “They must carefully track the end consumer of their products because the cost of cooperation with the aggressor will be high. This is also an example for governments whose businesses still supply goods to Russia, for sanctions to work, it is necessary to introduce a mechanism of inevitable punishment, as the United States has done.”
-554f0711f15a880af68b2550a739eee4.jpg)





-111f0e5095e02c02446ffed57bfb0ab1.jpeg)