- Category
- Latest news
France’s Navy Boosts Anti-Drone Training Amid Rising Threats in Red and Black Seas
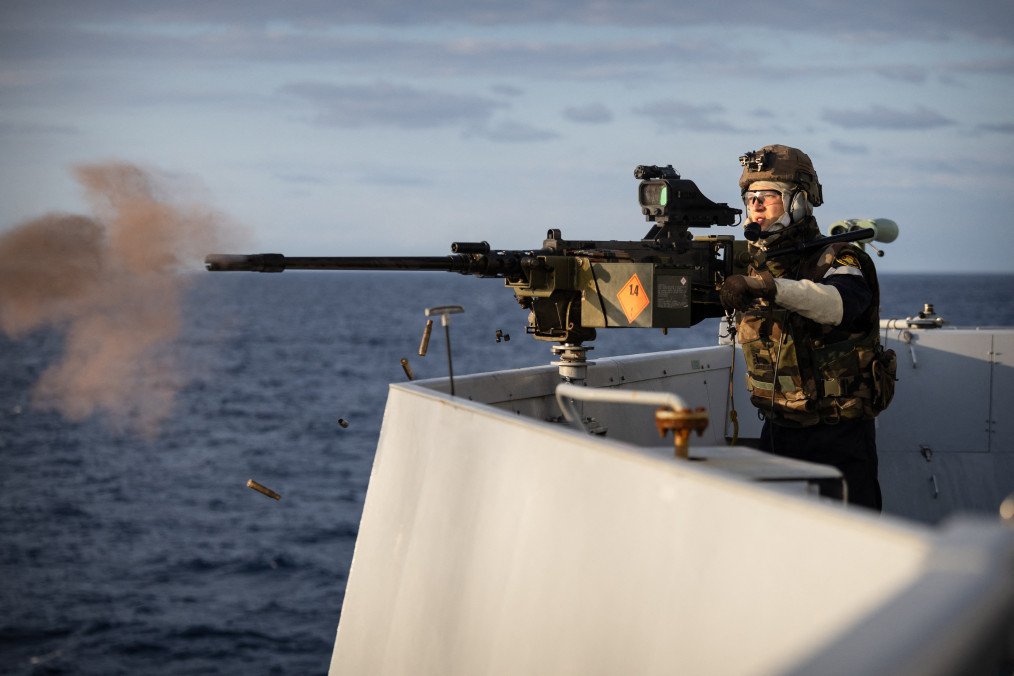

France’s Navy has stepped up training to counter air and sea drones, as new threats reshape global security—from Houthi rebel attacks on Red Sea shipping to Ukraine’s strikes on Russia’s Black Sea Fleet, Zone Militaire reported on October 6.
Drone warfare has become a defining challenge for modern naval operations, prompting France to focus its latest Wildfire exercises off the coast of Toulon on real-world defense scenarios.
According to Zone Militaire, the drills brought together six warships—including air-defense and multi-mission frigates, supply vessels, and La Fayette–class ships—supported by naval aviation units, fighter jets, and helicopters. The Royal Navy’s Wildcat helicopter, armed with Martlet missiles, also took part. In parallel, the French Air and Space Force simulated air raids under the Volfa exercise to coordinate with naval forces.
The Wildfire 25.2 exercises featured large-scale testing of cutting-edge anti-drone technologies. Among them were Denmark’s Tema 2D Scanter 6002 radar, the Exavision Seamos MR 5K electro-optical turret, and the MicrodB ALARM acoustic system. France’s Directorate General of Armaments provided 26 aerial and nine semi-rigid naval targets, while private operator Sea Owl deployed surface drones capable of operating in swarms. In total, 80 drone targets—aerial, surface, and underwater—were used in live-fire trials.
Captain Nicolas Forissier, commander of the FREMM frigate Provence, told Marine & Océans that armed drones and remote munitions are already transforming naval warfare, but swarms of underwater drones could pose an even more “formidable threat,” Zone Militaire.
During the drills, French forces tested all available countermeasures—from artillery and Martlet and Mistral missiles to GBU-12 bombs dropped by Atlantique 2 patrol aircraft.
Earlier, it was reported that since the start of Russia’s full-scale invasion, Ukraine developed two long-range cruise missiles—while the rest of Europe has produced only one comparable system, and that exists exclusively in a naval variant.





-72b63a4e0c8c475ad81fe3eed3f63729.jpeg)

